Pneumatic directional control valves are fundamental components in fluid systems that play a crucial role in regulating the flow of compressed air or gases. These valves are designed to control the direction of airflow within pneumatic circuits, allowing engineers and technicians to manage the movement and positioning of pneumatic actuators and devices. Here’s a brief overview of these essential components:
- Basic Functionality: Pneumatic directional control valves serve as switches that direct the flow of air or gas to different sections of a pneumatic system. They determine whether the air should flow to one actuator or another, enabling precise control over machinery.
- Types of Valves: There are various types of pneumatic directional control valves, including 2-way, 3-way, and 4-way valves. Each type has a specific function, such as on/off control or regulating the direction of airflow.
- Applications: Pneumatic directional control valves are used in a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and more. They are commonly found in automation systems, robotics, and other applications where precise control of pneumatic components is necessary.
- Importance: These valves are essential for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and accuracy of pneumatic systems. Proper selection and maintenance of pneumatic valves are critical for system performance.
In summary, pneumatic directional control valves are indispensable components in pneumatic systems, providing precise control over the direction of airflow. Whether you’re designing an automated production line or maintaining existing machinery, understanding the basics of these valves is vital for efficient pneumatic system operation. Pneumatic valves, including directional control valves, are at the heart of modern automation and industrial processes.
Key Components and Working Principles of Pneumatic Valves
Pneumatic valves are essential components in fluid control systems, allowing precise management of airflow and pressure. Understanding their key components and working principles is crucial for efficient system operation. Here’s a brief overview:
Key Components:
- Valve Body: The main structure of a pneumatic valve, typically made of metal or plastic, contains the other components.
- Actuator: Responsible for moving the valve, often through a diaphragm, piston, or solenoid, to control airflow.
- Ports: Inlet and outlet connections through which the fluid (usually compressed air) flows.
- Spool or Disc: The part that controls the flow by sealing or opening passages within the valve.
- Solenoid Coil: In electrically operated valves, the coil generates a magnetic field to actuate the valve.
Working Principles:
- Positioning: Pneumatic valves can be normally open (NO), normally closed (NC), or proportional, depending on their intended function.
- Actuation: When the actuator receives a signal (e.g., electrical current), it moves, causing the valve to change its state and control the fluid flow.
- Flow Control: The spool or disc inside the valve shifts, aligning with or blocking specific passages to regulate fluid flow.
- Directional Control: Pneumatic valves direct airflow by switching between different ports, allowing the fluid to go where it’s needed.
- Pressure Regulation: Some pneumatic valves have pressure-relieving features to maintain safe pressure levels within a system.
In summary, pneumatic valves play a pivotal role in fluid systems by regulating airflow and pressure. Understanding their key components and working principles is essential for optimizing the performance of these critical components in various industrial applications. When discussing pneumatic valves, it’s important to consider the specific needs of your system to select the most suitable type and configuration.
Types of Pneumatic Directional Control Valves Explained
Pneumatic valves play a pivotal role in regulating the flow of compressed air in various fluid systems. These valves are essential components in industrial automation, controlling the direction, flow, and pressure of air within pneumatic circuits. Understanding the different types of pneumatic directional control valves is crucial for selecting the right valve for your specific application. Here, we’ll explore the key types of pneumatic directional control valves:
- 2/2-Way Valves: These valves have two ports – one for air inlet and one for exhaust. They are commonly used to start and stop the flow of air in a system.
- 3/2-Way Valves: With three ports, these valves are suitable for diverting or stopping the flow of air by connecting one port to either of the two remaining ports.
- 4/2-Way Valves: These valves have four ports and are ideal for applications requiring two different actuator positions.
- 5/2-Way Valves: Widely used in pneumatic systems, these valves have five ports and two positions. They control the actuator’s movement in both directions.
- 5/3-Way Valves: Featuring three positions and five ports, these valves allow precise control of double-acting cylinders, making them suitable for applications that require intermediate positions.
- Solenoid-Operated Valves: These valves are controlled by an electromagnetic coil and are known for their rapid response, making them ideal for applications that require quick actuation.
- Manually Operated Valves: Manual valves offer simplicity and reliability, allowing operators to control the flow of air by hand.
Understanding the distinctions between these types of pneumatic directional control valves is essential for optimizing your pneumatic valve selection for fluid systems. Whether you need to start, stop, or redirect airflow, there’s a pneumatic valve type designed to meet your specific needs.
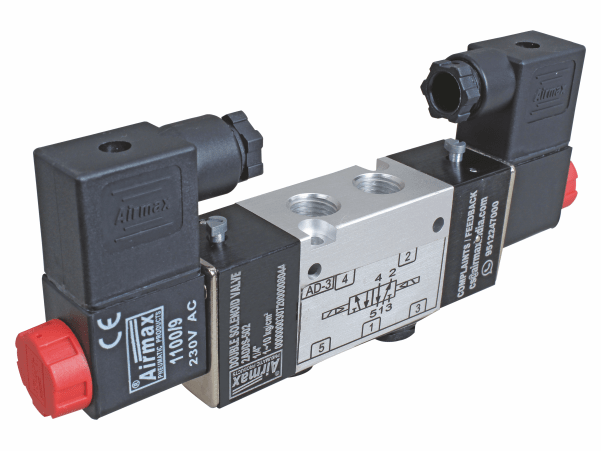
Applications of Pneumatic Valves in Fluid Systems
Pneumatic valves play a pivotal role in various fluid systems across industries due to their precision, reliability, and efficiency. These versatile components are used in a wide range of applications, enhancing control and automation in fluid handling processes. Here are some key applications of pneumatic valves in fluid systems:
- Manufacturing Automation: Pneumatic valves are employed in assembly lines to control the flow of fluids such as air, water, and hydraulic fluids. They facilitate precise movement and positioning of components, improving manufacturing efficiency.
- Chemical Processing: In chemical plants, pneumatic valves regulate the flow of corrosive and hazardous fluids. Their robust construction and resistance to chemical corrosion make them ideal for ensuring safety and accuracy.
- Water Treatment: Pneumatic valves are essential in water treatment facilities for controlling the flow of chemicals, sludge, and wastewater. They help maintain water quality and optimize treatment processes.
- Oil and Gas Industry: Pneumatic valves are used in pipelines and wellheads to control the flow of oil, gas, and other fluids. They ensure safe and efficient extraction, transportation, and processing of hydrocarbons.
- Food and Beverage Production: Pneumatic valves are crucial in the food and beverage industry for filling, packaging, and controlling the flow of liquids, gases, and ingredients.
- Agriculture: In agricultural applications, pneumatic valves regulate the flow of fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation water, enhancing crop yield and resource efficiency.
- HVAC Systems: Pneumatic valves control the flow of air, steam, and refrigerants in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, maintaining comfortable indoor environments.
In these diverse applications, pneumatic valves contribute to precise control, increased efficiency, and enhanced safety in fluid systems, making them an integral part of modern industrial processes. Whether in manufacturing, chemical processing, or environmental control, pneumatic valves continue to advance the capabilities of fluid handling systems.
Selecting the Right Pneumatic Valve for Your Fluid System
Choosing the appropriate pneumatic valve for your fluid system is crucial to ensure efficient and reliable operation. Pneumatic valves play a pivotal role in controlling the flow of gases or liquids within various industrial processes. To make an informed decision, consider the following factors:
1. Valve Type:
- Begin by understanding the different types of pneumatic valves available, such as solenoid valves, poppet valves, and spool valves.
- Evaluate which type aligns best with your specific application requirements.
2. Valve Size:
- Determine the size of the valve needed to handle the desired flow rate and pressure levels.
- Ensure it matches the pipe size and system capacity.
3. Valve Actuation:
- Choose between manual, electric, or pneumatic actuation methods, depending on your system’s automation needs and available power sources.
4. Material Compatibility:
- Consider the type of fluid your system will handle and select materials that are compatible with it to prevent corrosion or contamination.
5. Flow Control:
- Decide if precise flow control is necessary and opt for valves with appropriate flow adjustment features.
6. Environmental Conditions:
- Assess the environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to harsh chemicals, which might affect valve performance.
7. Reliability and Maintenance:
- Research the reliability and ease of maintenance of different valve brands and models.
- Choose valves from reputable manufacturers known for quality and durability.
8. Budget Considerations:
- Determine your budget constraints and seek a valve that offers the best balance between cost and performance.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the right pneumatic valve that optimally suits your fluid system, ensuring smooth and efficient operation while minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
Installation and Integration of Pneumatic Directional Control Valves
Proper installation and integration of pneumatic directional control valves are crucial to ensure the efficient operation of fluid systems in various industrial applications. Here’s a comprehensive guide with key points to consider:
1. Location and Mounting:
- Choose a suitable location for the pneumatic valve within the fluid system.
- Ensure secure mounting on a stable surface or bracket to prevent vibration and movement.
2. Piping and Tubing:
- Use compatible tubing and piping materials to connect the valve to the rest of the system.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for proper sizing to minimize pressure drops and maximize performance.
3. Directional Alignment:
- Align the valve’s directional ports with the intended flow path.
- Ensure the valve is oriented correctly, considering the desired flow direction.
4. Electrical Connections:
- Connect the valve’s solenoid or actuator to the appropriate electrical source.
- Ensure proper voltage and polarity to enable precise control.
5. Air Supply:
- Provide a clean and regulated air supply to the pneumatic valve.
- Use filters and regulators to maintain optimal air quality and pressure.
6. Control Interface:
- Interface the valve with the control system, such as PLCs or controllers.
- Verify that the control signals match the valve’s specifications.
7. Testing and Calibration:
- Perform thorough functional tests to ensure the valve operates as expected.
- Calibrate the valve if necessary to fine-tune its performance.
8. Safety Measures:
- Implement safety features such as emergency shutoffs and pressure relief valves in the installation.
- Train personnel on safe handling and operation procedures.
Properly installing and integrating pneumatic directional control valves not only ensures the reliability of your fluid system but also enhances its efficiency and safety, making it a critical aspect of any industrial setup where pneumatic valves play a key role.
Operation and Control: How to Use Pneumatic Valves Effectively
Pneumatic valves play a pivotal role in regulating the flow of compressed air and other gases within fluid systems. To harness their full potential and ensure optimal system performance, it’s crucial to understand how to operate and control pneumatic valves effectively. Here are key insights into this vital aspect:
- Valve Actuation: Start by comprehending the actuation methods available for pneumatic valves, such as solenoid, manual, or pilot-operated. Choose the one that suits your specific application needs.
- Pressure Regulation: Maintain a stable pressure environment. Pneumatic valves respond to pressure changes, so ensuring consistent pressure levels is essential for precise control.
- Proper Sequencing: Determine the sequence in which your valves need to operate. Proper sequencing prevents system inefficiencies and potential damage.
- Timing and Speed Control: Adjust the timing and speed at which pneumatic valves open and close to meet the desired operational requirements. This is crucial for applications with specific time-sensitive tasks.
- Feedback Systems: Implement feedback systems like sensors and transducers to monitor valve performance. This allows for real-time adjustments and troubleshooting.
- Emergency Shutdown Procedures: Establish emergency shutdown protocols to ensure the safety of your system in case of unexpected failures or emergencies.
- Regular Maintenance: Schedule routine maintenance to keep pneumatic valves in optimal condition. This includes cleaning, lubrication, and inspection.
Effective operation and control of pneumatic valves not only enhance system efficiency but also contribute to overall safety and longevity. By following these guidelines, you can make the most of your pneumatic valve system while ensuring its reliability and performance.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Pneumatic Directional Control Valves
Maintenance and troubleshooting of pneumatic directional control valves are critical aspects of ensuring the smooth operation of fluid systems. Proper care and timely diagnosis of issues can prevent costly downtime and maintain system efficiency. Here’s a 200-word content piece with bullet points on this topic:
Maintenance of Pneumatic Directional Control Valves:
- Regular Inspection: Schedule routine inspections to check for wear, leaks, and signs of damage on pneumatic valves.
- Lubrication: Ensure that lubrication is applied as recommended by the valve manufacturer to prevent friction and wear.
- Cleaning: Keep the valves clean from dirt and debris, which can clog or damage components.
Troubleshooting Pneumatic Directional Control Valves:
- No Air Flow: If there’s no airflow, check for blockages, damaged seals, or a malfunctioning solenoid.
- Leakage: Detects and repairs leaks by inspecting seals, O-rings, and connections.
- Valve Sticking: If the valve sticks in one position, examine the actuator and pneumatic lines for obstructions or damage.
- Inconsistent Operation: When valves operate inconsistently, inspect electrical connections, solenoids, and pneumatic pressure.
- Strange Noises: Unusual noises may indicate foreign objects or internal damage; disassemble and inspect the valve.
- Excessive Heat: Overheating valves can signal excessive friction or incorrect pressure; check for misalignment or worn parts.
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting practices help extend the lifespan of pneumatic directional control valves, ensure system reliability, and reduce unexpected downtime. Regular checks and prompt resolution of issues are essential for the efficient operation of fluid systems utilizing pneumatic valves. Remember that neglecting maintenance can lead to costly repairs and decreased overall system performance.
Safety Practices for Handling Pneumatic Valves in Fluid Systems
When working with pneumatic valves in fluid systems, ensuring safety is paramount. Mishandling these components can lead to accidents and system failures. To protect both personnel and equipment, follow these safety practices:
- Proper Training: Ensure that personnel responsible for handling pneumatic valves have received adequate training on their operation and maintenance.
- Wear Appropriate PPE: Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) such as safety goggles, gloves, and hearing protection as needed to safeguard against potential hazards.
- Valve Inspection: Regularly inspect pneumatic valves for signs of wear, damage, or leaks. Replace or repair faulty valves promptly.
- Pressure Release: Before servicing or disconnecting a pneumatic valve, release system pressure to prevent unexpected valve movement.
- Lockout/Tagout: Implement lockout/tagout procedures to isolate the valve from the air supply when performing maintenance to prevent accidental activation.
- Proper Tools: Use appropriate tools for valve installation and maintenance to prevent damage and ensure a secure fit.
- Avoid Overpressurization: Stay within the specified pressure limits for the pneumatic valve to prevent overpressurization and potential ruptures.
- Emergency Shutdown Procedures: Develop and communicate emergency shutdown procedures in case of valve malfunction or system emergencies.
- Regular System Checks: Conduct routine checks of the entire fluid system to identify and address potential issues before they escalate.
- Documentation: Maintain records of valve maintenance and inspection activities for future reference and compliance with safety standards.
By adhering to these safety practices, you can minimize risks associated with handling pneumatic valves in fluid systems, ensuring the safety of personnel and the integrity of your pneumatic valve systems.



